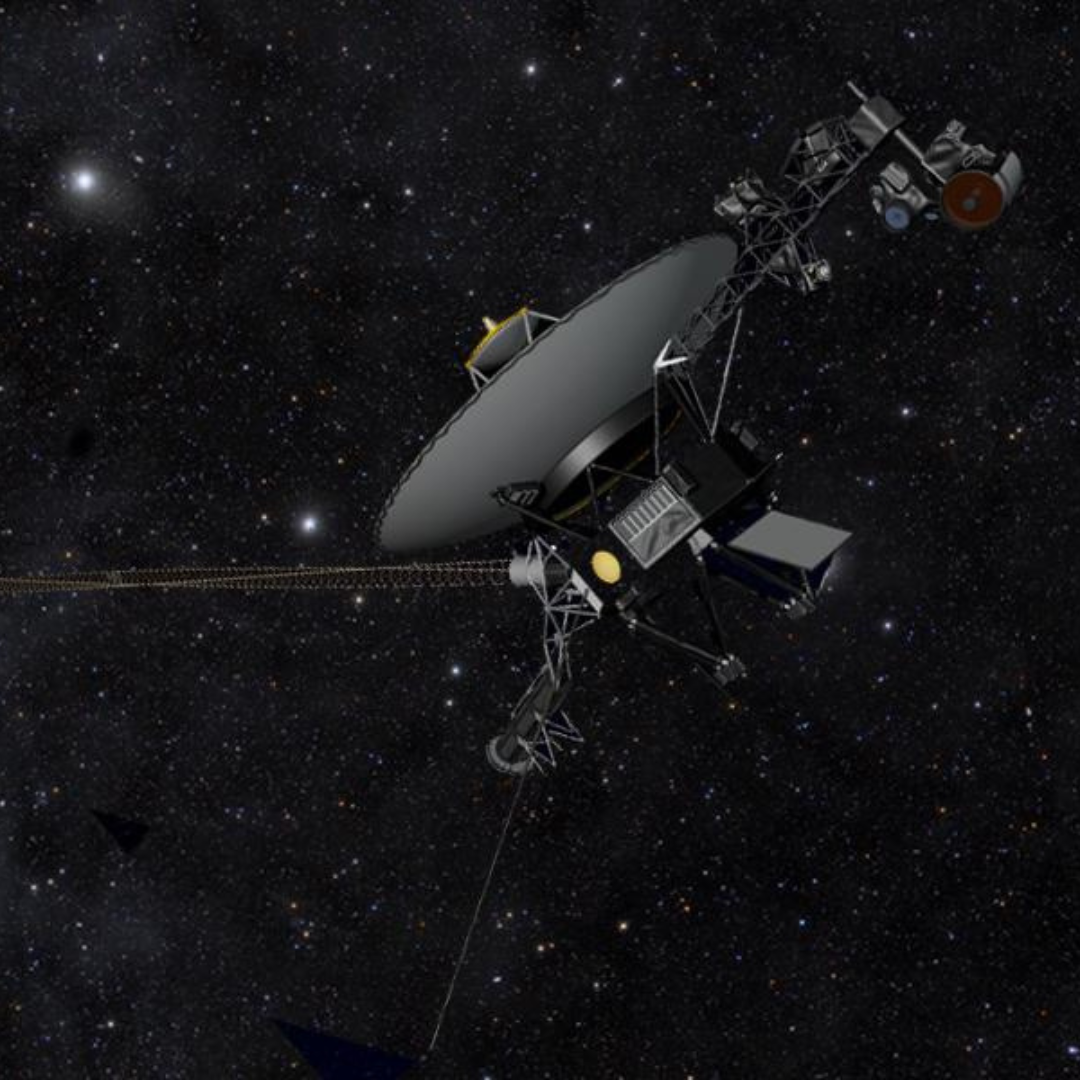
One of NASA’s most recognizable spacecraft, Voyager 1 started its trip on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program. Its primary purpose was to investigate the outer planets of the solar system, namely Jupiter and Saturn, but it accomplished much more than that, becoming the first artificial object to enter interstellar space.
Early Mission: Exploring the Outer Planets
Voyager 1’s first major successes came with its flybys of Jupiter and Saturn. It provided unprecedented images and data on these gas giants and their moons. Highlights include:
- Jupiter (1979): The first time volcanic activity was seen outside of Earth, Voyager 1 found active volcanoes on Io, one of Jupiter’s moons. Additionally, it returned fine-grained pictures of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot and its intricate moon and ring system.
- Saturn (1980): Voyager 1 provided scientists with breathtaking close-ups of Saturn’s moons and rings, particularly the mysterious Titan, whose dense atmosphere captivated them.
The Golden Record
The Golden Record, a 12-inch gold-plated copper disc with sounds and visuals designed to convey to any prospective extraterrestrial civilizations the richness of life and culture on Earth, is one of Voyager 1’s most well-known features. Natural sounds, music from many cultures, greetings in 55 languages, and encoded pictures of Earthly life are all included in the record.
Heading Toward the Edge of the Solar System
Voyager 1 proceeded into the outer limits of the solar system after its flyby of Saturn. Its 1990 acquisition of the Pale Blue Dot image, a picture of Earth taken from a distance of roughly 3.7 billion miles, was one of its last significant contributions before departing the planetary world. At Carl Sagan’s suggestion, the picture highlighted Earth’s vulnerability and its tiny position in the vast cosmos.
Entering Interstellar Space

Voyager 1 was the first spacecraft to leave the heliosphere—the bubble of solar wind and magnetic fields that envelops the planets—and enter interstellar space in August 2012. Voyager 1 is currently over 14 billion miles (23 billion kilometers) away from Earth and is still returning important information about this unexplored area of space. With this accomplishment, Voyager 1 becomes a leader in the human race’s search for planets outside of our solar neighborhood.
READ MORE: JAMES WEB SPACE TELESCOPE
Benchmark set by voyager 1
- Voyager 1 is currently more than 14 billion miles away from Earth, making it the farthest distant man-made object from our planet. This record demonstrates the long-term feasibility and engineering robustness of spacecraft designed for deep space exploration.
- First Probe in Interstellar Space: Voyager 1 became the first spacecraft to enter interstellar space in 2012 when it passed through the heliosphere’s edge. This milestone was a momentous accomplishment that gave humanity firsthand information from an area outside our solar system.
- Long-Distance Communication: By continuing to use the Deep Space Network to transmit data back to Earth from an unprecedented distance, Voyager 1 established a standard for long-distance communication. Future deep space mission planning has benefited greatly from this accomplishment.
Records
- First Up-Close Views of Outer Planets: Voyager-1 brought us the first up-close views of Jupiter and Saturn, revealing important details like the intricacy of Saturn’s rings and active volcanoes on Jupiter’s moon Io.

- The iconic Pale Blue Dot image, taken by Voyager 1 in 1990, highlights the immensity of space and the vulnerability of our planet by displaying Earth as a small dot from a distance of roughly 3.7 billion miles.
End of Journey
As of yet, Voyager-1 has not “died” Even though its power is waning, it is still operational and sending data as of 2024. The radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) that powers Voyager 1 produces less energy annually. The spacecraft is predicted to run out of power to run its scientific equipment by 2025, at which time it will stop transmitting data back to Earth. But it will carry on its lonely voyage into intergalactic space forever.
Voyager 1 Today
Despite having fewer instruments and weaker signals than it had in its heyday, Voyager 1 is still operational more than 40 years after it was launched. It is fueled by its radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) and is continuously sending data. Voyager 1 is predicted to keep providing useful data until about 2025, when its power source will eventually run out, despite its advanced age.
The mission of Voyager-1 has greatly increased our understanding of the solar system and continues to astonish us as it explores new territory. It represents human inquisitiveness, tenacity, and the unwavering desire to discover the unknown.
Conclusion
To sum up, Voyager-1 is a monument to human curiosity and inventiveness. In addition to making significant discoveries about the outer planets since its 1977 launch, it went above and beyond its original purpose in 2012 when it became the first spacecraft to traverse interstellar space. Its voyage has yielded priceless information that has changed our perception of the solar system and motivated upcoming generations of researchers and scientists. Its famous Golden Record, which reflects our culture and ideals, represents humanity’s longing to establish a connection with the cosmos. Voyager 1’s legacy lives on as it continues its silent journey across the vastness of space, serving as a constant reminder of both the limitless possibilities of exploration and discovery as well as our tiny but important place in the universe.












