Introduction
Word’s Most Expensive Indo-US NISAR Satellite When nations unite for the betterment of science, remarkable innovations emerge. The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) satellite, set for launch in March 2025, exemplifies such collaboration. This ambitious project, jointly developed by NASA and ISRO, is poised to revolutionize Earth observation. With a whopping $1.5 billion price tag, NISAR is the world’s most expensive Earth observation satellite, and its potential applications are as vast as its technological capabilities.
What is NISAR?
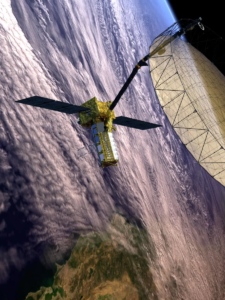
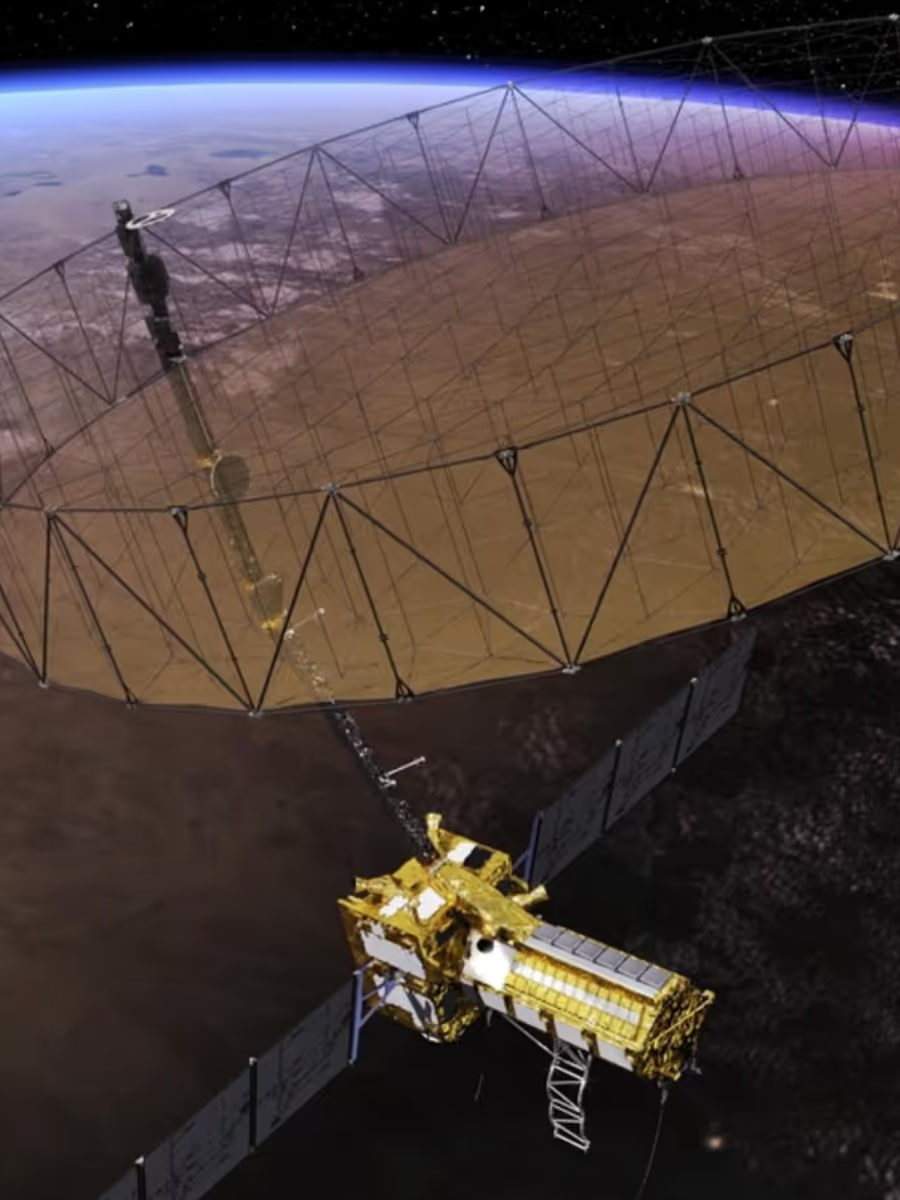
NISAR, short for NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar, is a groundbreaking satellite designed to provide precise and comprehensive Earth observation data. It employs advanced radar technology to monitor minute changes in the Earth’s land, water, and ice with unprecedented accuracy.
The primary aim of NISAR is to improve our understanding of natural hazards, climate change, and ecosystem dynamics. By capturing high-resolution images of the planet, NISAR will provide critical insights for scientific research and disaster management.
The Technology Behind NISAR
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)
At the core of NISAR’s capabilities is its Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) system. Unlike optical sensors, SAR can penetrate through clouds and operate during both day and night. This ensures consistent and reliable data collection regardless of weather conditions.
Dual-Frequency Radar
NISAR is equipped with dual-frequency radar systems—L-band and S-band. The L-band radar, contributed by NASA, excels at penetrating vegetation and providing detailed data on land changes. Meanwhile, the S-band radar, developed by ISRO, is optimized for detecting smaller surface-level changes, making the satellite highly versatile.
Why NISAR is Unique
NISAR’s dual-frequency radar system makes it the first of its kind. Its ability to provide continuous and detailed Earth observation data sets it apart from other satellites. This makes it an invaluable tool for monitoring natural disasters, environmental changes, and resource management on a global scale.
Indo-US Partnership: A Collaborative Milestone


The NISAR project symbolizes the strong partnership between NASA and ISRO, two of the world’s leading space agencies. While NASA contributes the L-band radar and key technologies, ISRO provides the S-band radar, satellite integration, and the launch vehicle. This collaborative effort combines the best of both agencies, showcasing how international cooperation can lead to groundbreaking achievements.
READ MORE:Six Planet Alignment in January 2025
Major Applications of NISAR
Disaster Management
Natural disasters like earthquakes, landslides, and floods cause widespread devastation. NISAR’s ability to detect subtle changes in the Earth’s surface can help predict and mitigate the impact of these events, potentially saving lives and reducing economic losses.
Climate Change Monitoring
With its capacity to observe ice sheets, forests, and other ecosystems, NISAR will play a pivotal role in tracking climate change. It will help scientists study how rising temperatures affect Earth’s resources and ecosystems.
Agriculture and Land Use
NISAR will provide valuable data for agricultural planning, such as monitoring crop health and mapping land use. This information will help farmers and policymakers optimize resource management.
Technical Specifications of NISAR
Size and Weight
NISAR is a large and robust satellite, weighing approximately 2,600 kilograms. It features a deployable reflector antenna with a diameter of 12 meters, making it one of the largest Earth observation satellites ever built.
Power and Hardware
The satellite is powered by advanced solar arrays and is equipped with state-of-the-art radar and data processing systems. These ensure seamless operation and real-time data transmission.
Cost and Funding
With an estimated cost of $1.5 billion, NISAR is the most expensive Earth observation satellite to date. NASA and ISRO share the financial responsibilities, with NASA funding the L-band radar and ISRO covering the S-band radar and the launch vehicle.
Launch Timeline and Location
NISAR’s development began in 2014, and after rigorous testing and validation, it is now ready for launch. The satellite will be launched aboard ISRO’s GSLV Mk II rocket from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, India, in March 2025.
How NISAR Benefits India

For India, NISAR represents a significant leap in technological advancement and scientific research. It will enhance the country’s ability to monitor natural resources, manage disasters, and contribute to global climate change studies. Additionally, the data generated by NISAR will support India’s agricultural planning and urban development initiatives.
How NISAR Benefits the USA
For the United States, NISAR offers a wealth of global observation data that can be used for disaster management, environmental monitoring, and scientific research. The project also strengthens the USA’s international space collaboration efforts, setting the stage for future partnerships.
Challenges in NISAR’s Development
Developing a satellite as advanced as NISAR came with its share of challenges.
- Technical Hurdles: Designing and integrating dual-frequency radar systems required overcoming significant engineering complexities.
- Budget and Time Constraints: The high cost and extended development timeline posed logistical challenges for both agencies.
Despite these obstacles, the project is on track for a successful launch, thanks to the collaborative efforts of NASA and ISRO.
Public and Global Impact
NISAR is not just a technological marvel; it’s a mission with far-reaching global implications. Its data will be freely accessible to researchers, policymakers, and industries worldwide. From improving disaster resilience to advancing climate research, NISAR promises to benefit humanity in countless ways.
Conclusion
As the world eagerly anticipates the March 2024 launch of NISAR, the satellite stands as a testament to international collaboration and technological innovation. With its unparalleled capabilities and wide-ranging applications, NISAR is set to transform how we monitor and understand our planet. This mission isn’t just about observing Earth—it’s about securing its future.
FAQs
Q1: What is the main purpose of the NISAR satellite?
A1: NISAR is designed to monitor changes in Earth’s surface, providing valuable data for disaster management, climate change research, and resource monitoring.
Q2: Why is NISAR considered the most expensive Earth observation satellite?
A2: Its advanced dual-frequency radar technology, extensive development timeline, and international collaboration contribute to its high cost of $1.5 billion.
Q3: What makes NISAR unique compared to other satellites?
A3: NISAR is the world’s first satellite equipped with dual-frequency radar, allowing it to capture highly detailed data in all weather conditions.
Q4: How will NISAR benefit India and the USA?
A4: India will gain enhanced disaster management and regional monitoring capabilities, while the USA will benefit from global observation data and strengthened international collaborations.
Q5: When and where will NISAR be launched?
A5: NISAR is scheduled for launch in March 2024 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, India.












